2020年4月29日,福建农林大学王琴教授在Annual Review of Plant Biology发表题为“Mechanisms of Cryptochrome-Mediated Photoresponses in Plants”的综述文章。
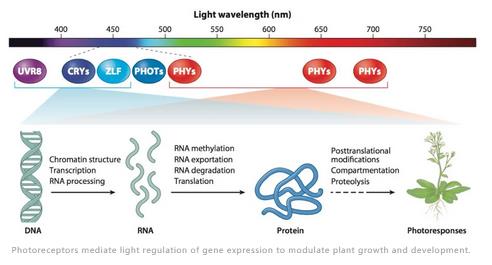
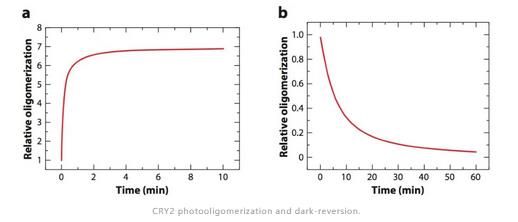
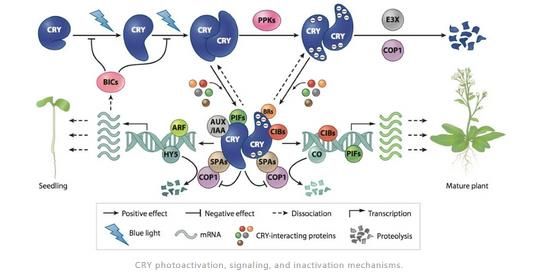
Cryptochromes are blue-light receptors that mediate photoresponses in plants. The genomes of most land plants encode two clades of cryptochromes, CRY1 and CRY2, which mediate distinct and overlapping photoresponses within the same species and between different plant species. Photoresponsive protein–protein interaction is the primary mode of signal transduction of cryptochromes. Cryptochromes exist as physiologically inactive monomers in the dark; the absorption of photons leads to conformational change and cryptochrome homooligomerization, which alters the affinity of cryptochromes interacting with cryptochrome-interacting proteins to form various cryptochrome complexes. These cryptochrome complexes, collectively referred to as the cryptochrome complexome, regulate transcription or stability of photoresponsive proteins to modulate plant growth and development. The activity of cryptochromes is regulated by photooligomerization; dark monomerization; cryptochrome regulatory proteins; and cryptochrome phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and degradation. Most of the more than 30 presently known cryptochrome-interacting proteins are either regulated by other photoreceptors or physically interacting with the protein complexes of other photoreceptors. Some cryptochrome-interacting proteins are also hormonal signaling or regulatory proteins. These two mechanisms enable cryptochromes to integrate blue-light signals with other internal and external signals to optimize plant growth and development.
论文链接:https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-100300











